Logic Reference
What is this Tutorial About?
This is a reference for all concepts studied in Classical Logic at LearnArabicOnline.com. Here we present brief summaries of the various discussions as well as the charts from the various logic tutorials . Charts that were left incomplete in their respective tutorials out of simplicity are now completed.
The Science of Logic
Definition | a science whose principles protect one from making mental mistakes |
Subject Matter | this is achieved by studying definitions and proofs |
Holy Grail | complete command of a type of proof known as the برهان |
Need | a primary but small subset of knowledge comes from senses and
experience, then the principles of logic are required to induce further
knowledge |
Status | one of the central sciences in Islamic and Greek academia whose
principles are seen extensively even in the Koran |
Other Designations | The Tool (because it is a ubiquitous tool used to judge between valid
and invalid thought processes), The Scale |
Pioneers | Aristotle, Farabi, Avicenna |
Things that exist and some that don’t | Their representations in our mind | Our expression of these representations | ||
علم
(مدلول) | –دلالة– | دال |
Semiosis (دلالة)
Types of Semiosis
دلالة
التزامية | دلالة
تضمنية | دلالة
مطابقية | |
the word “Washington” indicating on the president | the word “Washington” indicating on the Whitehouse | the word “Washington” indicates on the city thanks
to a naming process | دلالة
لفظية وضعية |
A person’s cough naturally indicates on distress | دلالة
لفظية طبعية | ||
Someone’s senseless noise in an adjacent room rationally indicates their presence therein | دلالة
لفظية عقلية | ||
A red hexagon indicates on stopping by coinage | دلالة
غير لفظية
وضعية | ||
A dog’s showing his teeth naturally indicates on
danger | دلالة
غير لفظية
طبعية | ||
Seeing smoke rationally indicates on fire | دلالة
غير لفظية
عقلية | ||
Types of Thought
علم
(مدلول) | ||
تصديق | تصور | |
immediately accepted claims (logic does not deal with these) | obviously understood concepts (logic does not deal with these) | بديهي |
claims that need to be proven (logic deals with these) | concepts that need to be defined (logic deals with these) | نظري |
The Indicating Coined Speech (دال) for Concepts
مفرد |
| ||||||
متكثر
المعنى | متوحد
المعنى |
| |||||
كلي
غير مشترك | كلي
مشترك | كلي | جزئي
حقيقي |
| |||
منقول | حقيقة/مجاز (literal / figurative) | كلي
مشكك | كلي
متواطي | ||||
The Indicated Idea (مدلول) for Concepts
Division by Universality
مدلول | |||||||||||
كلي | جزئي | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
عرض
عام | خاصة | |
Being Born is not unique to Human but
necessary and inseparable for it | Being More/Less Rational Than Another Human is unique to Human and cannot be
taken away from Humans | لازم |
Walking is not unique to Human and it can
be taken away (e.g. by injury) | Bipedal is unique to Human but it can be
taken away (e.g. by injury) | مفارق |
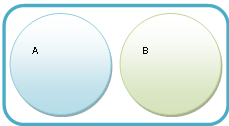
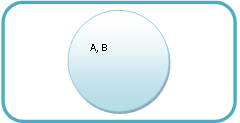
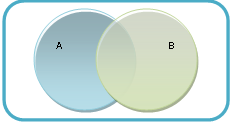
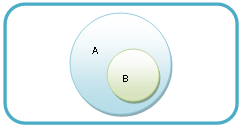
Relationship Between Universals
|
|
|
|
Definitions
قول
شارح | ||||
تعريف
حقيقي | تعريف
لفظي | |||
رسم
ناقص | رسم
تام | حد
ناقص | حد
تام | |
The Indicating Coined Speech (دال) for Assents
اللفظ
الدال | |||
مركب | مفرد | ||
مركب
ناقص | مركب
تام | … | |
إنشاء | قضية | ||
Categorized Based on Equation
قضية
حملية | |
حمل
بالاشتقاق | حمل
بالمواطاة |
Categorized Based on the Subject
قضية
حملية | |||
قضية
كلية . | قضية
شخصية Zaid is eating | ||
. . | كلية
طبعية men eat | ||
قضية
محصورة . | قضية
مهملة the men are eating | ||
موجبة
جزئية some of the men are eating موجبة
كلية all of the men are eating سالبة
جزئية some of the men are not eating سالبة
كلية all of the men are not eating | |||
Categorized Based on Affirmation & Negation
قضية
حملية | ||
غير
معدولة | معدولة | |
بسيطة | محصلة | ·
affirmative, affirmative subject, negative predicate ·
affirmative, negative subject, affirmative predicate ·
affirmative, negative subject, negative predicate ·
negative, affirmative subject, negative predicate ·
negative, negative subject, affirmative predicate ·
negative, negative subject, negative predicate |
Categorized Based on Modality
قضية
حملية | |
غير
موجهة | موجهة |
Simple Modalities
Explanation | Arabic Term | |
possible
(because the opposite is not necessary) | الممكنة
العامة | |
during
the time that the inherent attribute holds | الحينية
الممكنة | |
Necessary | الضرورية | |
unconditionally | الضرورية
المطلقة | |
so
long as the subject exists | ||
so
long as the subject is attributed with the intrinsic quality it bears | المشروطة
العامة | |
during
the inherently understood timeframe | الوقتية
المطلقة | |
during
some unspecified timeframe | المنتشرة
المطلقة | |
in
actual fact and not just potentially | المطلقة
العامة | |
in
actual fact and not just potentially, while the inherent attribute holds | الحينية
المطلقة | |
Not
necessary, but coincidentally perpetual | الدائمة
| |
unconditionally | الدائمة
المطلقة | |
so
long as the subject is attributed with the non-intrinsic quality it bears | العرفية
العامة | |
Compound Modalities
Explanation | Arabic Term |
necessarily
so long as the subject is attributed with the intrinsic quality it bears, but
not perpetually | المشروطة
الخاصة |
perpetually
so long as the subject is attributed with the non-intrinsic quality it bears,
but not perpetually otherwise | العرفية
الخاصة |
in
actual fact and not just potentially, but not out of necessity | الوجودية
اللاضرورية |
necessarily
in actual fact and not just potentially, but not perpetually | الوجودية
اللادائمة |
necessarily
during the inherently understood timeframe, but not perpetually | الوقتية |
necessarily
during some unspecified timeframe, but not perpetually | المنتشرة |
possible
(because both it and its opposite are not necessary) | الممكنة
الخاصة |
The Indicated Idea (مدلول) for Assents
Contradiction
Original | Contradictory |
universal | existential |
Original | Contradictory |
الضرورية
المطلقة | الممكنة
العامة |
الدائمة
المطلقة | المطلقة
العامة |
المشروطة
العامة | الحينية
الممكنة |
العرفية
العامة | الحينية
المطلقة |
Inverse
Original | Inverse | ||
Quantifier | Affirmativeness | Modality | |
Universal | Affirmative | الممكنة | |
الضرورية
المطلقة | Existential Affirmative حينية
مطلقة | ||
المشروطة
العامة | Existential Affirmative حينية
مطلقة | ||
الوقتية
المطلقة | |||
المنتشرة
المطلقة | |||
الدائمة
المطلقة | Existential Affirmative حينية
مطلقة | ||
العرفية
العامة | Existential Affirmative حينية
مطلقة | ||
Negative | الممكنة | ||
الضرورية
المطلقة | Universal Negative الدائمة
المطلقة | ||
المشروطة
العامة | Universal Negative العرفية
العامة | ||
الوقتية
المطلقة | |||
المنتشرة
المطلقة | |||
الدائمة
المطلقة | Universal Negative الدائمة
المطلقة | ||
العرفية
العامة | Universal Negative العرفية
العامة | ||
Existential | Affirmative | الممكنة | |
الضرورية
المطلقة | |||
المشروطة
العامة | |||
الوقتية
المطلقة | Existential Affirmative مطلقة
عامة | ||
المنتشرة
المطلقة | |||
الدائمة
المطلقة | |||
العرفية
العامة | |||
Proofs
حجة | ||||
قياس
ج. أقيِسة | استقراء | تمثيل | ||
دوران | سبر | |||
قياس | برهاني | premises are axioms or already proven theorems | |
جدلي | premises are widely accepted to be true, or accepted for the sake of
the argument | ||
خَطابي | premises are accepted to be true because they come from a trusted
authority | ||
شعري | premises are based on axioms that have been well-convinced | ||
سفسفطي | premises are plausible but deceptive axioms |
Syllogisms
If | And | Then | |
الشكل الاول | All of A is B | All of B is C | All of A is C |
All of A is B | None of B is C | None of A is C | |
Some of A is B | All of B is C | Some of A is C | |
Some of A is B | None of B is C | Some of A is not C | |
الشكل الثاني | All of A is B | None of C is B | None of A is C |
None of A is B | All of C is B | None of A is C | |
Some of A is B | None of C is B | Some of A is not C | |
Some of A is not B | All of C is B | Some of A is not C | |
الشكل الثالث | All of B is A | Some of B is C | Some of A is C |
All of B is A | None of B is C | Some of A is not C | |
Some of B is A | All of B is C | Some of A is C | |
Some of B is A | None of B is C | Some of A is not C | |
All of B is A | Some of B is not C | Some of A is not C | |
الشكل الرابع | All of B is A | Some of C is B | Some of A is C |
… | |||